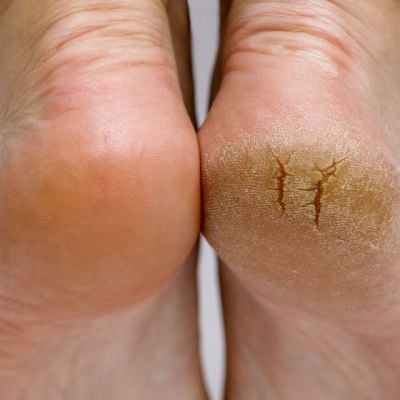
 Our feet, the foundation of our mobility, often bear the brunt of daily activities. Cracked heels, a common and often underestimated foot condition, can turn every step into a painful ordeal. This detailed guide will explore the causes, symptoms, and practical strategies for managing and preventing cracked heels. From understanding the underlying factors to adopting preventive measures, let's embark on a journey to heal and nurture our feet, ensuring each step is comfortable.
Our feet, the foundation of our mobility, often bear the brunt of daily activities. Cracked heels, a common and often underestimated foot condition, can turn every step into a painful ordeal. This detailed guide will explore the causes, symptoms, and practical strategies for managing and preventing cracked heels. From understanding the underlying factors to adopting preventive measures, let's embark on a journey to heal and nurture our feet, ensuring each step is comfortable.
Cracked Heels
What Are Cracked Heels?
Cracked heels, also known as heel fissures, occur when the skin on the heels becomes excessively dry and loses its elasticity. This section unravels the basics of this condition, exploring how factors like dehydration and external pressures contribute to the development of fissures.
Why Do They Occur?
Understanding the mechanisms behind cracked heels involves delving into why the skin on our heels is particularly prone to drying and cracking. We explore intrinsic and extrinsic factors, ranging from natural skin properties to environmental influences.
Common Causes of Cracked Heels
Dry Skin and Lack of Moisture:
Insufficient moisture is a primary factor in the development of cracked heels. We discuss how dry skin, often exacerbated by climate, improper foot care, or certain medical conditions, can compromise the skin's natural barrier function.
Prolonged Standing or Walking:
Occupations or lifestyles that involve prolonged periods of standing or walking can contribute to the formation of cracks on the heels. This section explores the impact of pressure and friction on the feet and how it can lead to heel fissures.
Footwear Choices:
Ill-fitting shoes or open-back footwear can worsen heel fissures or create conditions conducive to their development. We delve into how improper footwear choices contribute to cracked heels and offer insights into making foot-friendly choices.
Identifying Cracked Heels
Visual Indicators:
Cracked heels present with distinctive visual indicators. This section provides a detailed guide to recognizing symptoms such as visible cracks, redness, and, in more severe cases, bleeding or deep fissures that may extend into the dermal layers.
Associated Discomfort:
Beyond visual cues, cracked heels can cause discomfort, ranging from mild dryness to severe pain during weight-bearing activities. We explore the spectrum of sensations individuals may experience, helping readers gauge the severity of their condition.
Foot Care Essentials
The foundation of cracked heel prevention and management lies in hydration. We discuss the importance of regular moisturization, emphasizing emollients and creams that penetrate deep into the skin to restore moisture.
Gentle Exfoliation Techniques:
Gentle exfoliation helps remove dead skin cells, preventing the build-up that can exacerbate cracked heels. This section explores effective exfoliation techniques, including foot scrubs and pumice stones, while emphasizing the need for a delicate approach.
Soothing Soaks and Foot Baths:
Soothing foot soaks or baths can provide relief and facilitate healing. We delve into the benefits of incorporating ingredients like Epsom salts or essential oils, offering a relaxing and therapeutic experience for tired and cracked feet.
Home Remedies
Coconut Oil Magic:
With its nourishing properties, coconut oil is a popular remedy for cracked heels. We explore how applying coconut oil helps moisturize the skin, promote healing, and prevent future fissures.
Honey and Aloe Vera Soothe:
Combining honey and aloe vera is a potent remedy for cracked heels. This section outlines the healing properties of these natural ingredients and how their application can accelerate the recovery process.
Vitamin E Boost:
Vitamin E, renowned for its skin-nourishing qualities, is a valuable ally in cracked heel care. We discuss how incorporating vitamin E-rich oils or supplements can support skin health and prevent further dryness.
Footwear Choices
Optimal Shoe Selection:
Choosing the right shoes is paramount in preventing and managing cracked heels. We provide practical tips on selecting footwear with proper arch support, cushioning, and a comfortable fit, minimizing the risk of friction-induced fissures.
Open-Back Shoes: Pros and Cons:
While open-back shoes offer breathability, they may contribute to heel fissures. This section explores the pros and cons of open-back footwear, offering insights into how individuals can strike a balance between style and foot health.
Professional Care
Podiatric Assessment:
Persistent or severe cases of cracked heels may necessitate professional intervention. We discuss the role of podiatrists in conducting thorough foot assessments, identifying underlying causes, and recommending tailored treatment plans.
Medical Treatments: Prescription Solutions:
Medical treatments, including prescribed creams or ointments, may be recommended for stubborn cases. This section explores how prescription medications containing urea, salicylic acid, or other active ingredients contribute to skin healing.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle:
Adopting a holistic approach to foot health involves lifestyle adjustments. We discuss how staying hydrated, maintaining a balanced diet, and managing underlying health conditions contribute to overall skin health and prevent recurrent cracked heels.
Regular Foot Checks:
Regular self-examinations of the feet can be instrumental in identifying early signs of dryness or fissures. This section guides on performing thorough foot checks and incorporating them into routine self-care practices.
Diabetic Foot Care
Diabetic Foot Challenges:
Individuals with diabetes face specific challenges related to foot health. We explore how diabetes increases the risk of complications, emphasizing the importance of meticulous foot care, regular monitoring, and seeking professional advice.
Importance of Professional Monitoring:
Diabetic individuals benefit from regular foot assessments by healthcare professionals. This section details the significance of podiatric care in preventing and managing foot issues, including cracked heels, within the context of diabetes.
Conclusion
Cracked heels, though common, should not be dismissed as mere cosmetic concerns. Individuals can journey toward healing and maintaining healthy feet by understanding the causes, recognizing early symptoms, and adopting proactive measures. Whether through diligent foot care routines, natural remedies, or seeking professional advice when needed, the path to happy and healthy feet starts with knowledge and a commitment to self-care. With the insights gained from this guide, individuals can stride confidently, knowing that each step is toward nurturing and healing their feet from the ground up.
Disclaimer:
The information on this website is provided for educational and information purposes only and is not medical advice. Always consult with a licensed medical provider and follow their recommendations regardless of what you read on this website. If you think you are having a medical emergency, dial 911 or go to the nearest emergency room. Links to other third-party websites are provided for your convenience only. If you decide to access any of the third-party websites, you do so entirely at your own risk and subject to the terms of use for those websites. Neither Viera Podiatry, nor any contributor to this website, makes any representation, express or implied, regarding the information provided on this website or any information you may access on a third-party website using a link. Use of this website does not establish a doctor-patient relationship. If you would like to request an appointment with a health care provider, please call our office at (321) 253-4973.

